

- #POWERCHUTE BUSINESS EDITION HYPER V INTEGRATION HOW TO#
- #POWERCHUTE BUSINESS EDITION HYPER V INTEGRATION WINDOWS#
Since HGS needs to be isolated from fabric administrators, fabric AD forests fall very much into the unsuitable bucket. General purpose forests such as CORP AD forests are not suitable for use by HGS. These sort of forests are suitable and usually exhibit the following characteristics: they have very few admins, they are not general-purpose in nature and the frequency of logons are low. the forest used by Microsoft’s Privileged Identity Management solution. Suitable forests are likely purpose-built serving one sensitive function, e.g.

There are no particular technical requirements in order for an existing forest to be compatible with HGS’ needs but there are operational requirements and security-related best practices. For this reason, HGS typically resides in its own AD forest where the role is co-located with the domain controllers themselves. If this sounds like an appealing deployment option, ensure you’ve carefully considered that the HGS forest contains all of the servers running the HGS service and, therefore, it also contains the keys that can be used to compromise a shielded VM-in short, it’s contains the keys than can unravel a guarded fabric. not create its own forest during install. This is probably a good time to point out that HGS can also use existing AD forests, i.e. ) and a second forest that is automatically created when HGS is first installed ( In most scenarios, AD-based attestation will use two forests/domains: one forest to which the Hyper-V hosts are joined (the Let’s talk a bit more about how that looks and how it’s setup. With AD-based attestation, HGS measures only the group membership of the Hyper-V host that is attesting against it. Let’s go through the requirements and basic setup process for each of the two modes and wrap things up with the assurance (security promise) differences between them. TPM-based attestation (Trusted Platform Module)
#POWERCHUTE BUSINESS EDITION HYPER V INTEGRATION WINDOWS#
HGS supports two mutually-exclusive attestation modes:ĪD-based attestation (sometimes written as Windows Server Active Directory based attestation) HGS’ attestation mode is configured during installation (by using theĬmdlet) but can also be changed after the fact using the The process used to determine whether a Hyper-V host is healthy or not and the specifics of what we
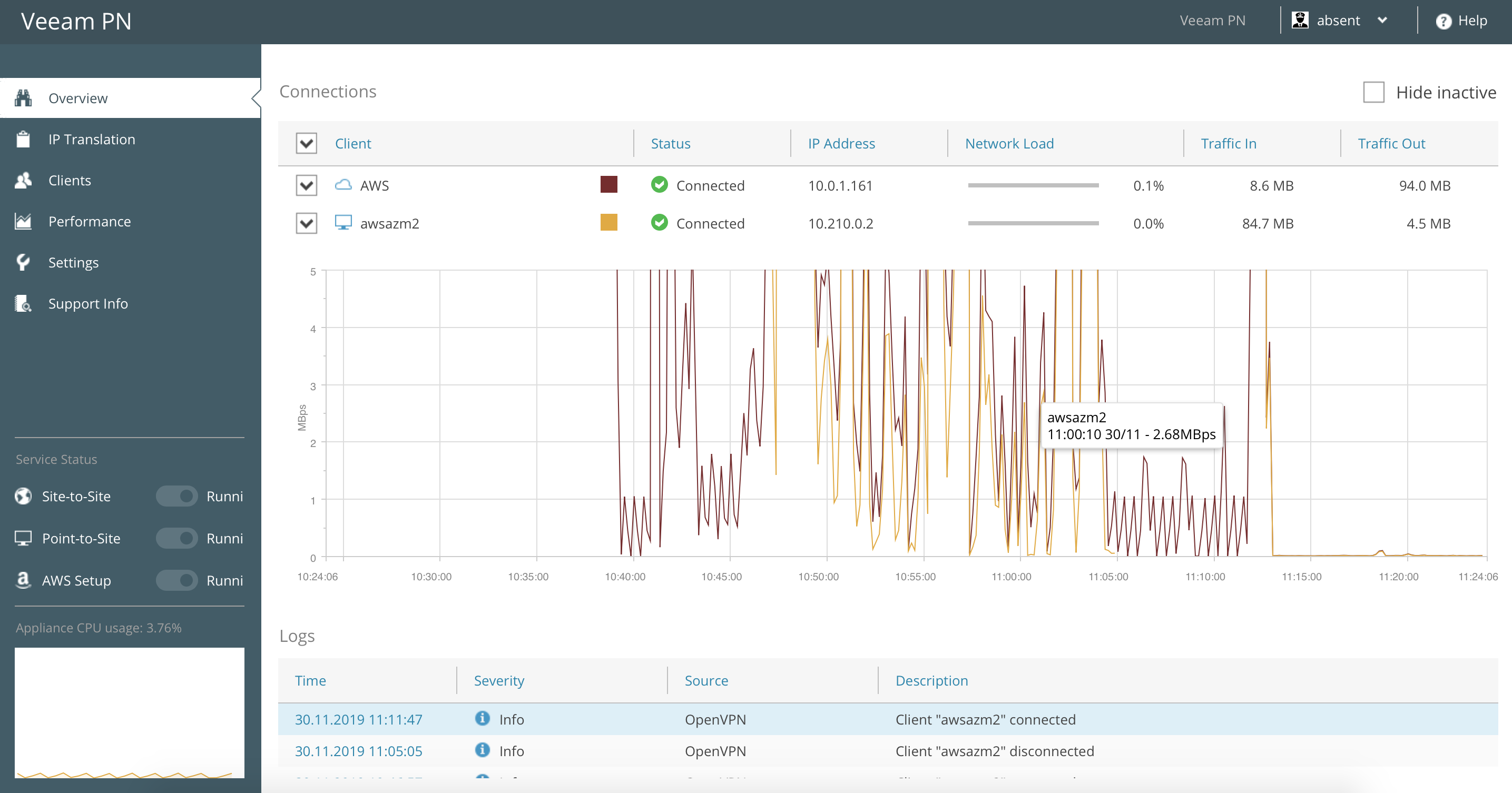
In the case of Shielded VMs, HGS serves as the external, trusted authority and is used to measure specific health characteristics of Hyper-V hosts in order to determine if they’re authorized (authorized because they’re healthy) to run Shielded VMs. Generally speaking, attestation is a process in which the health of a given computer is measured in some way-typically by an external, trusted authority. For more information about the HGS role and how it’s configured, see the blog post This blog describes the differences between HGS’ two mutually-exclusive attestation modes. The Host Guardian Service (HGS) is a new role in Windows Server 2016 that provides health attestation and key protection/release services for Hyper-V hosts running Shielded VMs. If you wish to allow Hyper-V to handle VM shutdown instead then enable the Automatic Stop action as outlined in steps 5 and 6 above.First published on TECHNET on Aug 16, 2016 Choose "Shut down the guest operating system".įor PowerChute Network Shutdown v3.1 and above, steps 5 and 6 are not required if you have enabled the VM shutdown option in PowerChute when Hyper-V Support has been enabled.Choose "Automatic Stop Action" option under Management.

Click on the Integration Services option and ensure “Operating System Shutdown” is enabled.
#POWERCHUTE BUSINESS EDITION HYPER V INTEGRATION HOW TO#
How to configure the shutdown of virtual machines when a Hyper-V host is commanded to shut down on Windows Hyper-V


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
